IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL Error is amongst the various errors which are classified under the BSOD or Blue Screen of Death error associated with the Windows Operating system. Blue screen of Death or BSOD errors tends to appear at the time of some severe issue with the Windows Operating system.
The presence of the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL Error in Windows 7, 8 or 10 is a sign that indicates that either some corrupted windows service is trying to access a particulate restricted memory location that triggered unauthorized access or simply the computer system is facing driver issues.
This situation leads to the inhibition of activities or the computer because the current login session gets terminated, and the computer screen will turn blue. A message of error will be seen.
It is advised for all the errors associated with the category to be fixed as soon as possible, as leaving the situation as it is for prolonged periods of time will result in the loss of data, among other things and system crashes.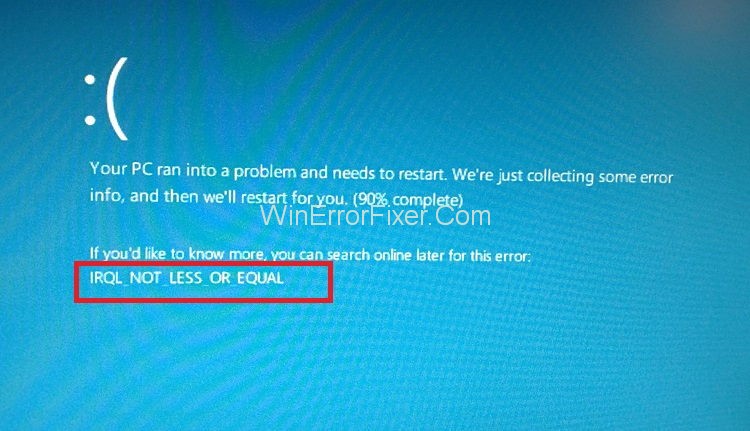
One of the major causes of IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error to occur are device drivers related issues, for example, the issue with hardware and registry, incompatibility and poor installation, virus, or malware attacks.
The best way to ensure that IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error does not occur is by ensuring the device driver and the Windows system are correctly installed and are up-to-date.
You can do so by performing regular checks for updates for the operating system along with a third party software, and backing up all the system files, is a very effective way to accomplish this.
Windows operating systems are highly evolved and relatively stable, yet from time to time, users might encounter the infamous ‘Blue Screen of Death’ (BSOD).
Among the myriad of error messages that might appear during a BSOD, “IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL” is one of the most common. Let’s dive into the intricacies of this error, its causes, and how to troubleshoot it.
What does IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL Mean?
IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL is a system error that occurs when a system process or a driver attempts to access a memory address without proper access rights. It’s essentially a way of the operating system saying, “Hey, something’s not right here!” It’s often associated with the BSOD, causing panic among users.
Common Causes of the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL Error:
- Faulty Device Drivers: Perhaps the most common reason. Outdated or wrongly configured drivers, especially graphics and network drivers, often lead to this error.
- Faulty Hardware: Bad RAM, malfunctioning CPUs, or even failing motherboards can trigger this error.
- Improper Software Installation: If a newly installed software conflicts with existing system files, it may result in this BSOD.
- Corrupt System Files: Critical system files, when damaged, can lead to this and other errors.
- Overclocking: Pushing your CPU or GPU beyond their limits can sometimes trigger this error, especially if not done correctly.
Fix IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL Error in Windows 10
The most efficient ways to tackle IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error are given below. Start with Method 1 and work down until one of these methods works for you. Let’s begin!
Solution 1: Disable Connected Devices and Drivers
Step 1: Unplug all of the devices that are connected to your computer including flash drives, USB sticks, etc. (All except for the keyboard and mouse.)
Step 2: Then disable related or other device drivers connected to your PC.
Step 3: Now, try to run your computer without any of the disabled devices being installed.
Step 4: Enable one device at a time and see if the error pops up after that.
Step 5: When the error appears after you enabled a device, it is an indication that that particular device/driver that you just enabled is the culprit and hence requires some action to be taken.
Step 6: Uninstall that driver in Safe Mode and then reinstall it afterwards. This method should resolve the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error.
Also Read:
- Potential Windows Update Database Error Detected
- DPC Watchdog Violation Error
- How to Uninstall Apps on Mac Computers
Solution 2: Use Safe Mode to Start the Computer
Step 1: First of all, click on the Shift + on-screen power button.
Step 2: Then click on Restart while pressing the Shift Key.
Step 3: Now click on Troubleshoot and then click on the Advanced Settings option.
Step 4: After that, click on Startup Settings.
Step 5: Now, click on Restart.
Step 6: Your computer will reboot now. After the reboot, you can choose the Safe Mode option.
Note: Even after following this method, you still see the error, then it’s a sign that there is no problem with any of the third-party apps, software, or device drivers. It also tells you that the problem is arising from the hardware of your computer.
Solution 3: Run System Restore
This method involves the creation of Restore Points before drivers and software being enabled in the case of emergencies as it allows you to restore the system without any data loss.
Step 1: First of all, go to Settings and click on the Update and Recovery option.
Step 2: Now, click on the Recovery option present on the left side of your computer screen.
Step 3: Then, click on Refresh this PC and then click on the Get Started option.
Step 4: Follow the instructions given on your screen after clicking it.
Solution 4: Debugging the RAM
This method requires the use of inbuilt utility to locate the problem within your hardware.
Step 1: Type Windows Memory Diagnostic in the search bar.
Step 2: Now, open the Windows Memory Diagnostic utility.
Step 3: This function will lead you to two options. You are required to select the Restart now and check for problems option. The scan may start either immediately or during another reboot session.
Step 4: This scan is going to show a list of issues or errors in the RAM or memory, which indicates that there is a need for replacing the RAM. Once it is replaced, the computer will function normally.
Solution 5: Disabling the memory cache
This could be done in two ways:
Solution 1.1:
Step 1: Use of Basic Input/ Output System feature. For this, you have to click on the BIOS set-up keys (this key varies from motherboard to motherboard. Although it is F2 in most of the computers)
Step 2: Now locate the option of Memory Settings and then disable the memory caching feature.
Solution 1.2:
Step 1: First of all, type Device Manager in the search bar.
Step 2: Now, click on the drop-down arrow present next to the option of Disk drivers, and then the name of a drive is going to show up.
Step 3: Then, double – click on the drive and navigate to the Policies Window.
Step 4: Click on the option that disables the driver.
Step 5: Click on, OK.
Step 6: At last, reboot your computer to make the made changes implement.
Solution 6: Using the Command Prompt feature to Fix corrupted files in Registry
Note: It is advised to back up the registry before performing this method.
Step 1: First of all, type cmd or Command Prompt in the Cortana search bar.
Step 2: Now, right-click on the Command Prompt. Click on Run as Administrator.
Step 3: A box will pop up, and you have to give the sfc/scannow command.
Step 4: At last, reboot your computer once the scan is finished.
What is Driver_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL on Startup?
This is a specific variant of the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error. It indicates that a driver has a mismatched interrupt request level (IRQL) and is trying to access an incorrect memory address on system startup. It’s primarily due to incompatible, outdated, or corrupt device drivers.
How Do I Fix the Blue Screen of Death?
- Update Device Drivers: Always ensure your device drivers, especially the graphics and network drivers, are updated. Use the device manager or the manufacturer’s website for updates.
- Check for Bad RAM: Tools like “Windows Memory Diagnostic” can check for issues in your RAM.
- System Restore: Restoring your system to a previous state can often solve the issue.
- Use the Windows System File Checker: Running
sfc /scannowin the command prompt can find and repair corrupted system files. - Avoid Overclocking: If you have overclocked your system, reverting to default settings might resolve the issue.
- Reinstall Windows: As a last resort, if other methods fail, reinstalling Windows can help.
Is IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL a Virus?
No, the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error itself isn’t a virus. However, malicious software can damage system files or drivers, which may lead to this and other errors. It’s always a good idea to run a thorough antivirus scan if you encounter frequent BSODs.
Recommended:
- io.netty.channel.AbstractChannel$AnnotatedConnectException:Connection refused: no further information Error on Minecraft
- confirm form resubmission
- Dragon Age Inquisition Won’t Launch Error
- Discord Screen Share Audio Not Working
Conclusion
This guide contains all the effective ways to resolve IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error. We hope this guide furthers your understanding of the reasons behind this error and the ways of dealing with it. Follow the instructions very carefully with the alert mind. We hope this guide proved useful to you, and your system is working fine now.
Though daunting, the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error is usually not a sign of any long-term damage to your computer. With a systematic approach to troubleshooting, most users can resolve this issue. Always remember to keep backups of essential data and regularly update your system and drivers to prevent such errors.



















