This article is about the BSOD Error Code: Memory_Management and the ways to fix it. The Blue Screen of Death (BSoD) is a recurring problem faced by Windows users. It occurs while restarting the computer when the system encounters an error during a background process.
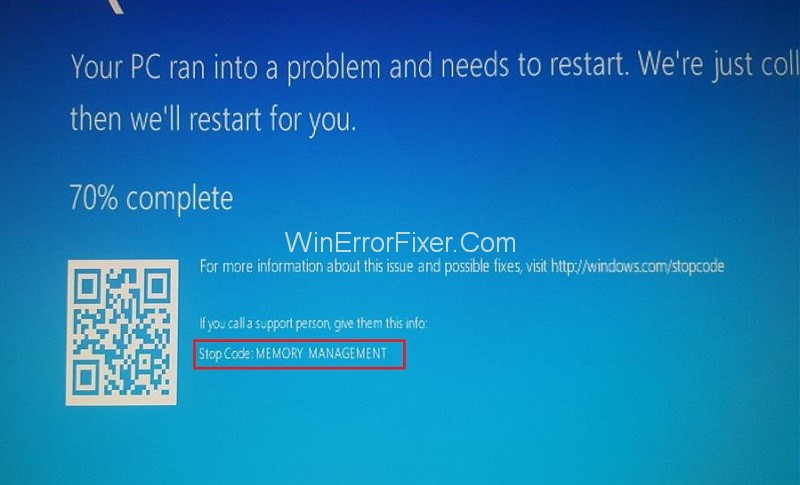
A blue screen appears with the message, “Your PC ran into a problem and needs to restart. We’re just collecting some error info, and then we’ll restart for you”.
It may be a one-time error and get resolved after a restart, but often it may keep occurring. Among the countless errors which cause the BSoD, one is the Memory_Management error. Its stop code or error code is 0x0000001A.
Memory management is a critical component in computer systems, ensuring optimal performance and stability. Whether you’re working with operating systems, software development, or understanding computer architecture, a strong grasp of memory management is essential.
In this article, we explore what memory management is, its key requirements, popular techniques, its characteristics, and why it is so crucial.
What Is Windows Memory_Management?
A computer’s Memory_Management is the process that manages or regulates the device’s memory usage. It monitors every transmission of memory between the RAM and the physical memory for execution. It regulates every byte of memory is allocated to any of the processes. When the user closes any program, the memory is reallocated to some other process.
It also frees up any amount of memory that is not in use. The background processes of the system constantly use a lot of memory, and that, too, is regulated. In short, Memory_Management is a crucial feature of the system for its normal functioning.
What is Used for Memory Management
Memory management involves a range of techniques and hardware components. The computer’s operating system is primarily responsible for memory management, often with the support of additional software tools.
Memory management hardware may include Memory Management Units (MMUs), while algorithms like paging, segmentation, and partitioning are commonly used methods for handling memory.
What Causes The Memory_Management Blue Screen Error
The Memory_Management process may often encounter a problem, thus causing the Blue Screen of Death. There is no fixed reason for the Memory_Management blue screen error. Some of the common causes of this error can be summarized as follows:
- System files may be corrupted.
- Hardware may be damaged, or face other issues.
- RAM may be having issues.
- Drivers may be corrupted or outdated.
- The hard disk may be having problems.
These problems may be, in turn, caused by a number of factors. Issues with drivers may arise after a Windows OS update due to incompatibility. System files may be corrupted due to malware. The above-mentioned factors then cause a number of errors, including that of Memory_Management blue screen.
How to Fix Memory_Management (Blue Screen of Death) Error
Since there are a number of possible causes of the error, there are solutions based on those causes. If you are facing the Blue Screen due to Memory_Management, try the solutions below.
Solution 1: Update Windows 10
Updating your Windows OS often helps resolve most problems. To check whether there is any pending update, proceed as follows:
Step 1: Go to Settings in the Start menu, or by pressing Windows key + I.
Step 2: Select the option Update and Security
Step 3: In the Windows Update section, check for any available update. Install it if available.
Since the system will reboot during the update process, make sure to save all tasks and files beforehand.
Solution 2: Run Windows 10 Memory Diagnostic Tool
The Memory_Management error is very likely to have been caused by a RAM problem. To detect any such problem, run the Windows Memory Diagnostic program. Following are the steps to run this tool:
Step 1: Open Windows Memory Diagnostic by directly searching it in the Windows search bar. Alternatively, open it by typing “mdsched.exe” in the Run dialogue box (open it by pressing Windows + R).
Step 2: In the small Windows Memory Diagnostic window, select the option “Restart Now and check for problems.” Save all your pending tasks and files before proceeding.
Alternatively, select the other option “Check for problems the next time I start my computer” if you are not ready to restart at the moment. Then restart later.
Step 3: Once the diagnostic tool has concluded its process, any error in the RAM will be detected.
Step 4: Since the log file is not easily visible, it has to be viewed separately. For this purpose, first press Windows + X, then select Event Viewer on the menu.
Step 5: Next, navigate to Event Viewer (Local) → Windows Logs → System
Step 6: Click on Find from the left panel. A box will appear, write “MemoryDiagnostic” in it. Now, this will display the diagnostic results.
We can use the Memory Diagnostic tool only for finding the error in the RAM. Furthermore, to fix the error, take note of the error codes detected, and take the help of Google for solutions.
Solution 3: Update Your Drivers
The Memory_Management error may also be due to the outdated system drivers. Updating your drivers may thus fix the error. To check the status of the drivers and update them if necessary, follow the steps below:
Step 1: Press Windows key + X and go to select Device Manager in the menu.
Step 2: In the Device Manager window, locate the drivers and check if there is any yellow error symbol. If there is, they need updates. If there is no error symbol, the drivers are not the cause of the Memory_Management error.
Step 3: To install driver updates, it is best to use a Driver Update tool or software. You can download such software from various online sources for free. They will automatically install updates to all the drivers.
After the update installation is complete, restart the system and check whether the Memory_Management error is solved.
Solution 4: Run MemTest86
In case Windows Memory Diagnostic fails to detect any RAM error, but you still suspect some problem with the RAM, there exists another tool. You can use the MemTest86 for a deeper memory test to detect any error in the RAM of x86 computers. Following are the steps to conduct this test:
Step 1: Download the MemTest86 tool (in ISO format) from its official site.
Step 2: Create a bootable flash drive (many free tools are available online to create one). Then write the MemTest86 tool to the flash drive.
Step 3: Reboot into your system using the bootable flash drive to launch MemTest86.
Step 4: Wait until the process is complete. It may take a few hours, depending on the RAM size.
As in the previous method, note down the errors displayed after the MemTest86, if any. Then search them on Google to find further solutions to them.
Solution 5: Run CHKDSK
A problem in the hard disk may be another possible cause of the issue. To scan for any disk problem and repair it, follow the instructions below:
Step 1: Open Command Prompt as administrator. Search “cmd” in the Windows search bar, then click “Run as administrator.”
Step 2: Write the command given below and hit Enter:
chkdsk c: /f /r
If the system file is in any other drive, mention that drive instead of.
Step 3: The scan may not be possible immediately if the system file is in C, the primary drive, as it is in use. You will be asked if you want to schedule the scan for the next system reboot: type y to answer yes, and press Enter.
Step 4: Restart the system. The scan will then start automatically. Once complete, check whether the Memory_Management error has been rectified.
Solution 6: Run SFC
Another way to resolve this issue is to conduct a System File Checker (SFC) scan. If any corrupted system file is the cause of the problem, it may be detected. Following are the steps to conduct an SFC scan:
Step 1: Search “Command Prompt” in the Windows search bar, then right-click on the Command Prompt option and select “Run as administrator.” Also, you can press Windows + X to open it. Then select Command Prompt (Admin) on the menu.
Step 2: In the Command Prompt window, type the command “sfc /scannow” and hit Enter to run. This process will continue for about 15 to 30 minutes.
Step 3: It will detect and repair the corrupted files in the system and then, restart the system.
Solution 7: Check Device’s Hardware
There is a chance of physical damage to the hardware in case of any recent movement of the device. Manually checking the hardware for such damage is an option. Place it properly in the CPU. It may be easy in case of a desktop device, but more complicated if it’s a laptop. Take the help of a technician if necessary.
Solution 8: Reset Windows 10
If somehow none of the above methods yield any result, there is the last option – to reset the Windows OS. This should rectify any issue with the system files. While this process will involve a loss of certain data, your personal files will be retained. Follow the steps below for a system reset:
Step 1: Open Settings from the Start menu or by pressing Windows + I.
Step 2: In Settings, go to Update and Security.
Step 3: In the left panel, select Recovery.
Step 4: In the Recovery section, click on “Get Started” under “Reset this PC.”
Step 5: Select “Keep my files” option. Windows OS will then go through the reset process.
The Five Requirements of Memory Management
- Relocation: Memory addresses must be dynamically mapped to physical locations.
- Protection: Ensures that one program cannot interfere with another, maintaining system stability.
- Sharing: Allows multiple programs to use the same set of data.
- Logical Organization: Memory must be allocated in a way that it meets the logical requirements of a program.
- Physical Organization: This involves the actual allocation of memory space.
Three Memory Management Techniques
- Paging: Involves dividing the computer’s main memory into fixed-size blocks, or ‘pages’, and mapping them to virtual memory as needed.
- Segmentation: This technique divides memory into varying-length blocks, or ‘segments’, according to the program’s needs.
- Contiguous Memory Allocation: This involves allocating a single contiguous block of memory to a program.
Characteristics of Memory Management
- Efficiency: A robust memory management system will use hardware and software resources efficiently.
- Flexibility: Memory management should adapt to different types of processes and system loads.
- Speed: Quick memory allocation and deallocation are crucial for optimal system performance.
- Safety: Protecting the memory spaces of different programs from each other is paramount.
- User Transparency: Ideal memory management should require minimal user intervention.
Importance of Memory Management
- Optimal System Performance: Efficient memory management ensures that the system performs tasks quickly and efficiently.
- Resource Utilization: It helps in making sure that the computer’s memory resources are used optimally.
- Data Protection: Proper memory management safeguards against unauthorized data access.
- Program Execution: Effective memory management ensures that programs run smoothly, without crashes or slowdowns.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It can also lead to cost savings by reducing the need for additional memory resources.
Recommended:
Conclusion
Thus, we have discussed the various techniques to fix the Blue Screen of Death caused by Memory_Management. It can occur due to several reasons. Depending on the exact cause of the error, any of the above methods should yield results.
Remember to try the option of resetting the Windows OS only as a last resort. Ideally, at least one of the simpler techniques should work.



















